UNESCO is an international organisation whose aim is the promotion of education, science, culture, communication and information. It gives the title of World Heritage Site to places that qualify due to their uniqueness and authenticity. They also have a so-called Black List for those places that are threatened by grave danger.
Here are the last 11 beautiful places in the world you should visit as soon as possible:
Part 4/4 (status 18.03.15)
Index:
Fortifications on the Caribbean Side of Panama: Portobelo-San Lorenzo (2012).34
Liverpool – Maritime Mercantile City (2012).35
Timbuktu (2012).36
Tomb of Askia (2012).37
Ancient City of Aleppo (2013).38
Ancient City of Bosra (2013).39
Ancient City of Damascus (2013).40
Ancient Villages of Northern Syria (2013).41
Crac des Chevaliers and Qal’at Salah El-Din (2013).42
East Rennell (2013).43
Site of Palmyra (2013).44
11 Beautiful places in the world that will be gone soon/4:
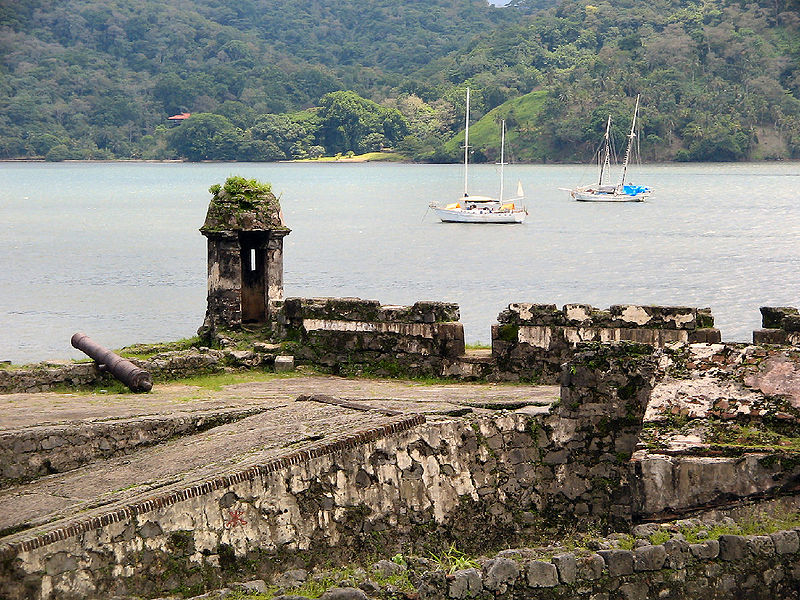
34. Fortifications on the Caribbean Side of Panama: Portobelo-San Lorenzo (map)
What are the fortifications of Panama? Portobelo is a port city in Colón Province, Panama, established during the Spanish colonial period. It has a deep natural harbor and was used as a center for silver exporting before the mid-eighteenth century. Today Portobelo is a sleepy city with a population of fewer than 3,000. In 1980 the ruins of the Spanish colonial fortifications, along with nearby Fort San Lorenzo, were designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Why were they added? For environmental factors, lack of maintenance and urban development.
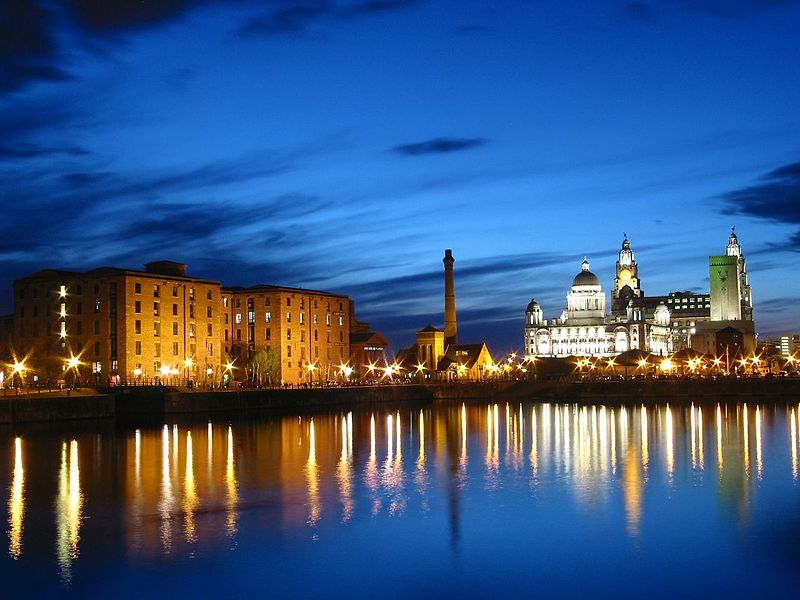
35. Liverpool – Maritime Mercantile City (map)
What is Maritime Mercantile City? The Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City is a Site in Liverpool, England. It comprises six locations in the city centre of Liverpool including the Pier Head, Albert Dock and William Brown Street, and includes many of the city's most famous landmarks. UNESCO received the city council's nomination for the six sites in January 2003 for the fact that it was 'the supreme example of a commercial port at a time of Britain's greatest global influence'.
Why was it added? In 2012, the site was inscribed Due to the proposed redevelopment of historic docklands known as Liverpool Waters.
36. Timbuktu (map)
What is Timbuktu? Timbuktu is a city in the West African nation of Mali. The town is the capital of the Timbuktu Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali. It had a population of 54,453 in the 2009 census.
Why was it added? Because of the Threat by armed conflict.
37. Tomb of Askia (map)
What is the Tomb of Askia? The Tomb of Askia, in Gao, Mali, is believed to be the burial place of Askia Mohammad I, one of the Songhai Empire's most prolific emperors. UNESCO describes the tomb as a fine example of the monumental mud-building traditions of the West African Sahel. The complex includes the pyramidal tomb, two mosques, a cemetery and an assembly ground. At 17 metres in height it is the largest pre-colonial architectural monument in the region. It is the first example of an Islamic architectural style that later spread throughout the region.
Why was it added? Also because of the Threat by armed conflict.
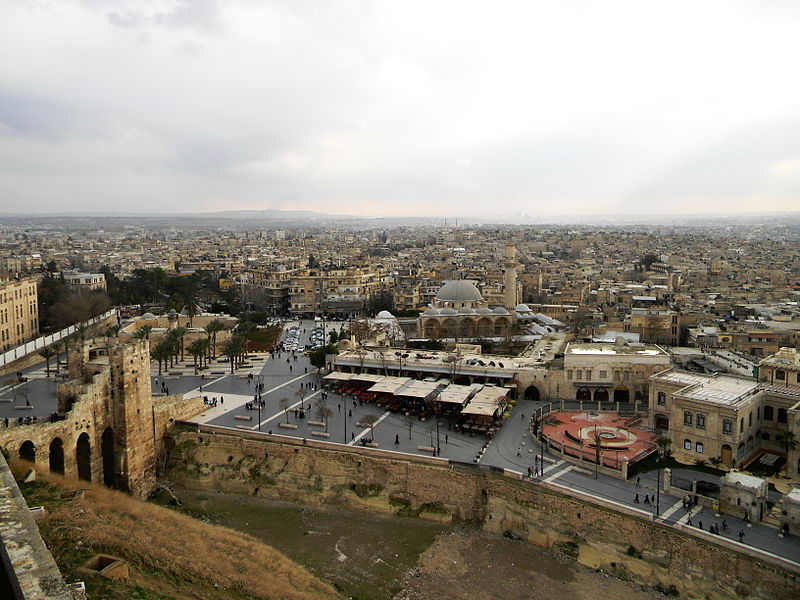
38. Ancient City of Aleppo (map)
What is the ancient city of Aleppo? The Old City of Aleppo is the historic city centre of Aleppo, Syria. Many districts of the ancient city remained essentially unchanged since its construction during the 12th to the 16th century. Being subjected to constant invasions and political instability, the inhabitants of the city were forced to build cell-like quarters and districts that were socially and economically independent. Each district was characterized by the religious and ethnic characteristics of its inhabitants. The Old City of Aleppo -composed of the ancient city within the walls and the old cell-like quarters outside the walls- has an approximate area of 350 hectares (3.5 km²) housing more than 120,000 residents. Characterized with its large mansions, narrow alleys, covered souqs and ancient caravanserais, the Ancient City of Aleppo became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1986.
Why was it added? In February 2014, the opposition groups of the Islamic Front claimed responsibility for destroying a series of major historic buildings in the old city including the justice palace, the Carlton hotel and the old building of the city council.
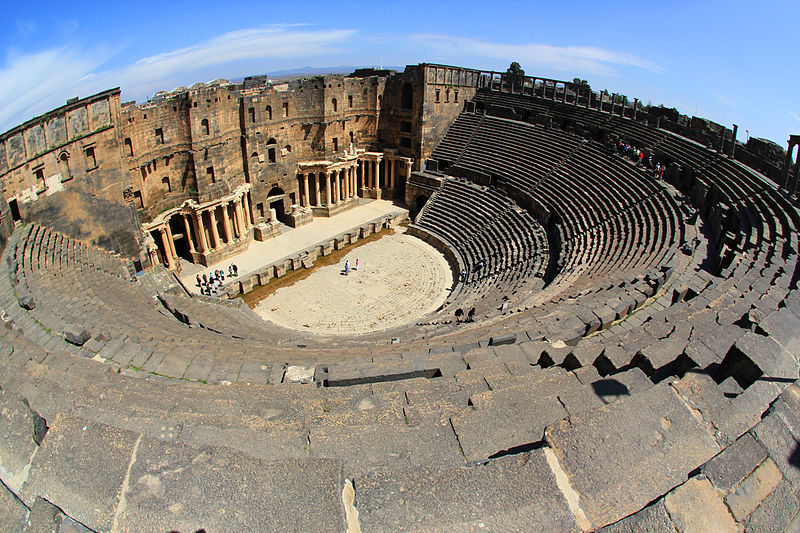
39. Ancient City of Bosra (map)
What is the ancient city of Bosra? Bosra is a town in southern Syria. Bosra's inhabitants are predominantly Muslims. Bosra has an ancient history and during the Roman era it was a prosperous provincial capital. It continued to be administratively important during the Islamic era, but became gradually less prominent during the Ottoman era. Today, it is a major archaeological site and has been declared by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
Why was it added? Because there was/is war down there.
40. Ancient City of Damascus (map)
What is the ancient city of Damascus? Damascus is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major cultural and religious center of the Levant. The Barada River flows through Damascus. During Ottoman rule, the city decayed completely while maintaining a certain cultural prestige. Today, it is the seat of the central government and all of the government ministries.
Why was it added? Also because of the Military conflict.
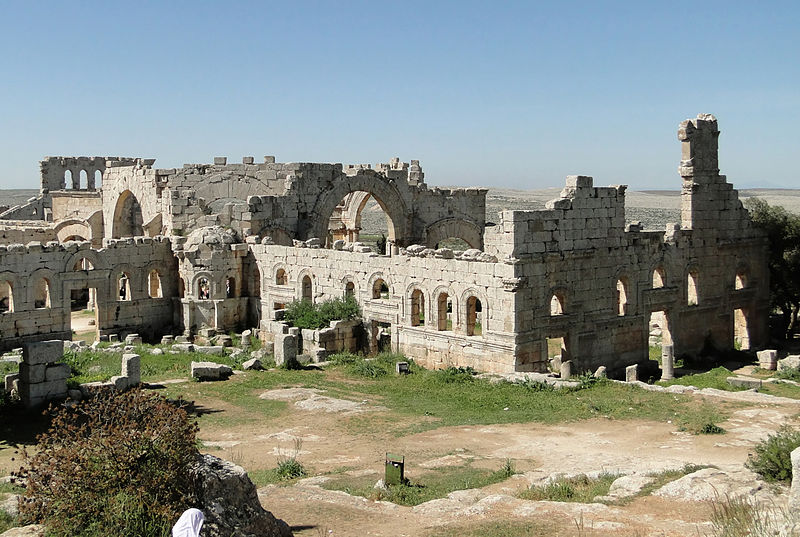
41. Ancient Villages of Northern Syria (map)
What are the ancient villages of northern Syria? The Dead Cities or Forgotten Cities are a group of 700 abandoned settlements in northwest Syria. Most villages which date from the 1st to 7th centuries, became abandoned between the 8th and 10th centuries. The settlements feature the well-preserved architectural remains of dwellings, pagan temples, churches, cisterns, bathhouses etc. These ancient settlements cover an area 20–40 km (12–25 mi) wide and some 140 km (87 mi) long. The Massif includes three groups of highlands: the first is the northern group of Mount Simeon and Mount Kurd; the second middle group is the group of Harim Mountains; the third southern group is the group of Zawiya Mountain.
Why were they added? Military conflict.
42. Crac des Chevaliers and Qal’at Salah El-Din (map)
What is Crac des Chevaliers and Qual'at Salah El-Din? Krak des Chevaliers is a Crusader castle in Syria and one of the most important preserved medieval castles in the world. And the Citadel of Salah Ed-Din is also a castle in Syria. In high mountainous terrain on a ridge between two deep ravines and surrounded by forest, the site has been fortified since at least the mid 10th century. In 2006, the castles of Qal'at Salah El-Din and Krak des Chevaliers was recognised as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. The site is owned by the Syrian government.
Why is it on the list? As every site in Syria because of the military conflict.
43. East Rennell (map)
What is east Rennell? East Rennell is the southern portion of Rennell Island in the Solomon Islands. Rennell is the largest raised coral atoll in the world and the area in East Rennell surrounding Lake Tegano contains many endemic species.
Why is it on the list? Because of the threat of logging activities to the site's outstanding universal value and its effect on the local ecosystem.
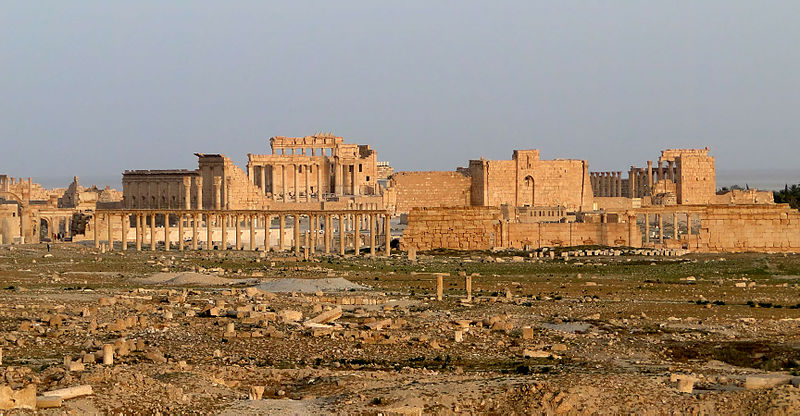
44. Site of Palmyra (map)
And lastly what is the site of Palmyra? Palmyra was an ancient Arabic city in central Syria. It had long been a vital caravan stop for travellers crossing the Syrian desert and was known as the Bride of the Desert. Though the ancient site fell into disuse after the 16th century, it is still known as Tadmor in Arabic. There is a newer town of the same name next to the ruins. The Palmyrenes constructed a series of large-scale monuments containing funerary art such as limestone slabs with human busts representing the deceased.
Why the heck was it added? Also because of the military conflict there.















Comments